Urea
Urea Description

Urea (carbamide), readily produced from ammonia and carbon dioxide, is a very important chemical in the agricultural and the polymer industries.
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic. Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. introduction and scientific invention of Urea is identified as a life changing event in the history of agriculture. Urea N46% is the world’s most common nitrogen fertilizer and has been used uniformly in all the agricultural lands of the world. Never before this, agriculture had seen such booming heights in production as well as prosperity. Urea is neutral in pH and can adapt to almost all kinds of soils. It is a waste product formed naturally by metabolizing protein in humans as well as other mammals, amphibians and some fish. Urea is widely used in the agricultural sector both as a fertilizer and animal feed additive.
The last decade has seen urea (carbamide) as a superb replacement to ammonium nitrate and has unleashed new unsurpassed production records. The white, crystalline solid comprises of a proportionate compound mixture of more than one nutrients and contains 46% nitrogen. Farmers have identified with this chemical fertilizer as a great ladder to huge success in agro revolution. The nutrient composition rendered by urea enhances the productivity of the soil and enriches its nutrient constituency. Providing each plant with relevant elements needed, urea sustains plant life.
More than 90% of world industrial production of urea is destined for use as a nitrogen-release fertilizer. Urea has the highest nitrogen content of all solid nitrogenous fertilizers in common use. Therefore, it has the lowest transportation costs per unit of nitrogen nutrient. Urea fertilizers rapidly transform to the ammonium form in soils.
Worldwide, urea N46% is one of the most widely used dry granular sources of nitrogen. It is preferred by the fertilizer manufacturing industry since it is relatively easy to manufacture. Urea also has a high nitrogen content (46%), in comparison to other popular nitrogen sources (i.e. ammonium nitrate). On a ton for ton basis, urea contains 35% more nitrogen than ammonium nitrate. This has implications on the storage and transport of nitrogen fertilizer products. Carbamide is considered a relatively stable product to store and transport, and it is for this reason that the transportation of Carbamide is considered very cost effective in comparison to its most common alternative, ammonium nitrate.
Advantages of Carbamide Fertilizer
– Superior Nitrogen content
– Low production cost, as source is natural
– Non-flammable and risk-free storage
– Wide application range, for all types of crops and soils
– Neutral pH and harmless to crops and soil
In 2022, the potential supply of urea fertilizers is expected to reach 197 million metric tons. Increasing crop prices lead to increased fertilizer demands and has been especially noted in recent years in South Asia. Favorable weather also increases demand for fertilizers in major agricultural regions.
Urea Uses
Urea is the world’s most commonly used nitrogen fertilizer and indeed more of it is manufactured by mass than any other organic chemical. Containing 46% N, it is the most concentrated nitrogen fertilizer, and is readily available as free-flowing prills (granules). It is the cheapest form of nitrogen fertilizer to transport and it is also the least likely to ‘cake’. It is therefore favoured in developing countries.
While over 90% of urea produced is used as a fertilizer, it has other uses, which include the manufacture of the melamine, used in melamine-methanal resins. Urea itself also forms important resins.
An increasingly important use of Carbamide is in reducing air pollution from diesel engines in cars, buses and lorries. Diesel engines run at high temperatures and nitrogen and oxygen, from the air, are able to react together under these conditions to produce high concentrations of nitric oxide. One way to remove this pollutant is to allow it to react with ammonia to form nitrogen.
However it is not possible to use ammonia directly as it is too volatile and is poisonous. Instead a solution of urea in water is injected into the hot gases emerging from the engine in the exhaust. It is thermally decomposed to ammonia and carbon dioxide. This is the reverse of the process used to make ammonia:
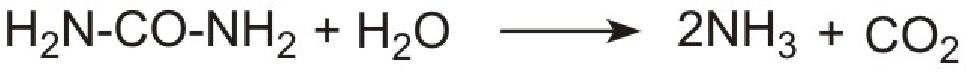
Unlike ammonia, urea is safe and easy to handle. The products, ammonia and carbon dioxide, together with the exhaust gases, are passed immediately over a catalyst in the exhaust system. Ammonia reduces the oxides of nitrogen (mainly nitric oxide), formed in the combustion processes, to nitrogen. The process is complex but the overall reaction can be represented thus:
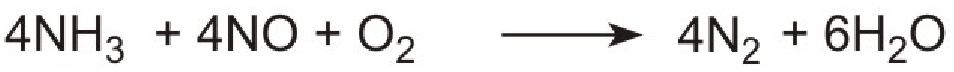
The system is known as Urea SCR (urea-based selective catalytic reduction) and can reduce pollution by nitrogen oxides to almost zero.
Annual Production of Carbamide
| World | 164 million tons |
| China | 62 million tons |
| India | 23 million tons |
| Middle East | 20 million tons |
| Rest of Asia | 18 million tons |
| FSU | 12 million tons |
| North America | 9.5 million tons |
| Europe | 9.5 million tons |
Urea Specifications
| Typical Chemical Analysis |
| Parameter Specification |
| Total Nitrogen Content, % 46.0 |
| Moisture content, wt. % 0.1 – 0.4 |
| Biuret, wt. % 0.85 – 1.5 |
| Conditioning agent, wt. % 0.30 – 0.60 |
| Typical Physical Properties |
| Parameter Specification |
| Bulk density, lb/ft3 48 – 52 |
| Angle of repose 28 – 32o |
| Size Guide Number (SGN) see note 1 240 – 320 |
| Uniformity Index (UI) see note 1 50 – 55 |
Packing of Carbamide N46
Packing in 50 kg polypropylene bags accepted up to 2000mt, for more quantities Bulk is available.
